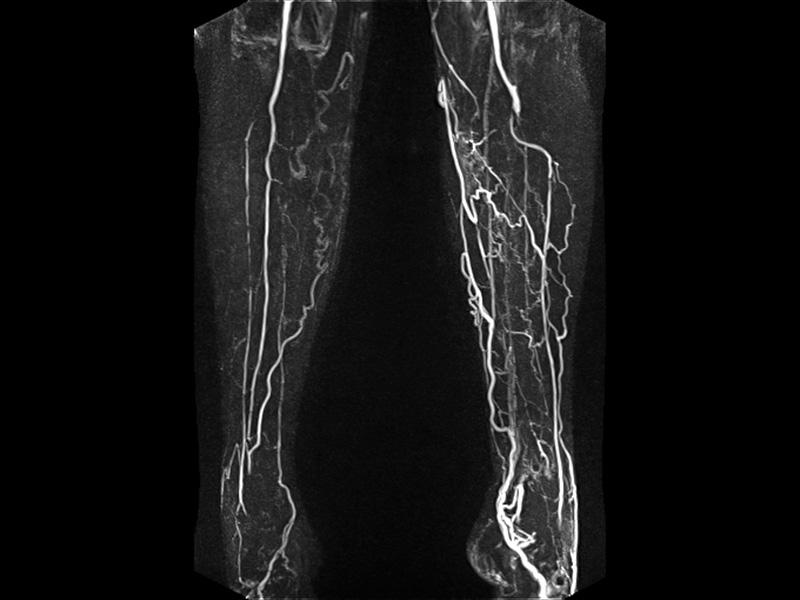
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) uses the techniques of a standard MRI to evaluate blood vessels and help identify abnormalities. Such abnormalities can be stenosis (abnormal narrowing), occlusions, and/or aneurysms (vessel wall dilatations, at risk of rupture). The most common areas of the body that are evaluated with MRA include the arteries of the neck & brain, the thoracic and abdominal aorta, the renal arteries, and the legs.
MRA is a non-invasive imaging technique and does not use radiation, though it may require an injection of contrast material. The contrast material used for MRA is less likely to cause an allergic reaction than the contrast material used for computed tomography (CT).